Electrical engineering technology
Electrical engineering technology
The following texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
Electrical engineering technology
- Mention the difference between core and shell type transformers.
In core type , the windings surround the core considerably and in shell type the core surround the winding.
- What is the purpose of laminating the core in a transformers ?
To reduce eddy current loss.
- Give the emf equation of a transformer and define each term
Emf induced in primary coil E1 = 4.44 fΦ mN1 volt
Emf induced in secondary coil E2 = 4.44fΦ mN2 volt
Where f is the frequency of AC input
Φ m is the maximum value of flux in the core
N1, N2 are the number of primary and secondary turns.
- Does the transformer draw any current when secondary is open ? Why ?
Yes,it (primary) will draw the current from the main supply in order to magnetise the core and to supply
iron and copper losses on no load . There will not be any current in the secondary since secondary is open.
- Define voltage regulation of a transformer
When a transformer is loaded with a constant primary voltage , the secondary voltage decreases for lagging
power factor load, and increases for leading pf load because of its internal resistance and leakage reactance . The change
in secondary terminal voltage from no load to full load expressed as a percentage of no load or full load voltage is termed
as regulation .
% regulation down = (0V2-V2) x 100/0V2
% regulation up = (0V2-V2) x 100/V2
- Full load copper loss in a transformer is 1600 watts. What will be the loss at half load ?
If x is the ratio of actual load to full load then copper loss = x2(full load copper loss)
Here Wc = (0.5)2 x 1600 = 400 watts
- Define all day efficiency of a transformer .
It is the computed on the basis of energy consumed during a certain period , usually a day of 24 hrs.
ηall day = output in kWh /input in kWh for 24 hrs.
- Why transformers are rated in kVA ?
Copper loss of a transformer depends on current and iron loss on voltage . Hence total losses depends on Volt-
Ampere and not on the power factor. That is why the rating of transformers are in kVA and not in kW.
- What are the typical uses of auto transformer ?
(i)To give small boost to a distribution cable to correct for the voltage drop.
(ii)As induction motor starters.
(iii)As furnace transformers
(iv)As interconnecting transformers
(v)In control equipment for single phase and 3 phase elective locomotives.
- What are the applications of a step-up and step-down transformers ?
Step-up transformers are used in generating stations. Normally the generated voltage will be either 11 kV or 22 kV.
This voltage is stepped up to 110 kV or 220 kV or 400 kV and transmitted through transmission lines. (In short it may
Be called as sending end).
Step-down transformers are used in receiving stations. The voltage are again stepped down to 11 kV or 22 kV and
transmitted through feeders.(In short it may be called as receiving end).
Further these 11 kV or 22kV are stepped down to 3 phase 400 V by means of a distribution transformer and made available at consumer premises.
The transformers used at generating stations and receiving stations are called power transformers.
- How transformers are classified according to their construction ?
Or
Mention the difference between “CORE” and “SHELL” type transformers.
Or
What are the two types of cores used ? Compare them.
Transformers are classified according to their construction as ,
(i)Core type (ii)Shell type (iii)Spirakore type.
Spirakore type is a latest transformer and is used in big transformers.
In “core” type, the windings(primary and secondary)surround the core and in “shell” type, the core surround the
windings.
- Explain on the material used for core construction.
The core is constructed of transformer sheet steel laminations assembled to provide a continuous magnetic path
with a minimum of air gap included. The steel used is of high silicon content sometimes heat treated to produce a high
permeability and a low hysteresis loss at the usual operating flux densities.the eddy current loss is minimized by laminating
the core, the laminations being insulated from each other by light coat of core-plate vanish or by an oxide layer on the
surface .the thickness of laminations varies from 0.35 mm for a frequency of 59 Hz and 0.5 mm for a frequency of 25
Hz.
- When will a Bucholz relay operate in a transformer ?
Bucholz rely is a protective device in a transformer. If the temperature of the coil exceeds its limit, Bucholz relay
operates and gives an alarm.
- How does change in frequency affect the operation of a given transformer ?
With a change in frequency, iron loss, copper loss, regulation, efficiency and heating varies and thereby the
Operation of the transformer is affected.
- What is the angle by which no-load current will lag the ideal applied voltage ?
In an ideal transformer , there are no copper loss and no core loss,(i.e. loss free core). The no load current is only magnetizing current. Therefore the no-load current lags behind by an angke of 90˚. However the windings possess resistance and leakage reactance and therefore the no-load current lags the applied voltage slightly less than 90˚.
- List the advantages of stepped core arrangement in a transformer .
- To reduce the space effectively.
- To obtain reduced length of mean turn of the windings.
- To reduce I2R loss.
- Why are breathers used in transformers ?
Breathers are used to entrap the atmospheric moisture and thereby not allowing it to pass on to the transformer
oil. Also to permit the oil inside the tank to expand and contract as its temperature increases and decreases.
Also to avoid sledging of oil i.e. decomposition of oil. Addition of 8 parts of water in 1000000 reduces the insulations
quantity of oil. Normally silica gel is filled in the breather having pink colour. This colour will be changed to white due
to continuous use, which is an indication of bad silica gel, it is normally heated and reused.
- What is the function of transformer oil in a transformer ?
Nowadays instead of natural mineral oil, synthetic oils known as ASKRELS (trade name ) are used. They are
noninflammable, under an electric arc do not decompose to produce inflammable gases. PYROCOLOR oil possess
high dielectric strength. Hence it can be said that transformer oil provides , (i)good insulation and (ii)cooling .
- A 1100/400 V, 50 Hz single phase transformer has 100 turns on the secondary winding. Calculate the number of
turns on its primary.
We know V1 / V2 = k = N2 / N1
Substituting 400/1100 = 100/N1
N1 = 100/400 x 1100
= 275 turns.
- What are the functions of no-load current in a transformer ?
No-load current produces flux and supplies iron loss and copper loss on no-load.
- How will you transfer the quantities from one circuit to another circuit in a transformer ?
1.Secondary to primary 2.Primary to secondary
Symbol Value Symbol Value
V2 ̉ V2/k VL ̉ kV1
I 2̉ kI2 IL ̉ I1 /k
R2 ̉ R2/k2 RL ̉ k2R1
X2 ̉ X2/k2 XL’ k2X1
ZL ̉ ZL/k2
- Define voltage regulation of a transformer.
When a transformer is loaded with a constant primary voltage , the secondary voltage decreases for lagging
factor load, and increases for leading power factor load because of its internal resistance and leakage reactance.
Let oV2 = secondary terminal voltage at no load
= E2 = kE = kV because of no load the impedence drop is negligible
V2 = secondary terminal voltage on full load.
The change in secondary terminal voltage from no load to full load is = oV2 – V2.This change divided by oV2 is known
regulation down. If this chane is divided by V(i.e full load secondary terminal voltage ) then it is called as regulation
up.
%regulation down =[(oV2 – V2)/oV2 ]*100
and
%regulation up =[(oV2 – V2)/V2]*100
- Can the voltage regulation of a transformer go to negative? If so under what condition?
Yes. If the load has leading power factor.
- Distinguish between power transformer and distribution transformer .
Power transformers have very high power ratings in the order of mVa. They are used in generating and receiving
stations. Sophisticated controls are required. Voltage ranges will be very high. Distribution transformers are used in
consumer side. Voltage levels will be medium. Power ranging will be small in order of kVA. Complicated controls
are not needed.
- What is the purpose of providing ‘taps’ in transformer and where these are provided?
In order to attain the required voltage , ‘taps’ are provided. Normally it will be provided at low voltage side.
- What is prime mover?
The basic source of mechanical power which drives the armature of the generator is called prime mover.
- Give the materials used in machine manufacturing
Three materials are used in machine manufacturing.
(i)steel – to conduct magnetic flux
(ii)copper – to conduct electric current
(iii)Insulation
- What is torque proportional to?
Torque is proportional to the interacting fields and to the sine of the electrical space angle between their magnetic axes.
- How will you find the direction of emf using Fleming’s Right Hand Rule?
The thumb, the forefinger and the middle finger of the right hand are held so that these fingers are mutually perpendicular, then
Forefinger - Field
ThuMb - Motion
Middle finger- I,current
- How will you find the direction of force produced using Fleming’s Left Hand Rule?
The thumb , forefinger and middle finger of the left hand are held so that those fingers are mutually perpendicular then
Forefinger - Field
ThuMb - Motion(due to force)
Middle finger - I,current
- Which type of d.c armature winding requires equalizer rings?
Lap winding
- How are armature windings classified based on the placement of the coil inside the armature slots?
Single layer winding and
Double layer winding
- Write down the emf equation for d.c generator.
E = (фNZ / 60)(P/A) V
Where P= number of poles
Z= Total number of conductors
A= number of parallel paths
Ф= flux per pole
N= speed in rpm
- Why the armature core in d.c machines is constructed with laminated steel sheets instead of solid steel steel?
Steel sheets offer low relutance path for the magnetic field , laminated sheets reduce eddy current loss.
- Why is commutator employed in d.c machines?
- Conduct electricity between armature and fixed brushes
- Converts altenating emf into unidirectional emf and vice versa
- Distinguish between shunt and series field coil constructions.
Shunt field coils are wound with wires of small cross section and have more number of turns. Series field coils are wound with wires of larger cross section and have less number of turns.
- How does a d.c motor differ from d.c generator in construction?
Generators are normally placed in closed room , accessible only to skilled operators. Therefore on ventilation point
of view they may be constructed with large opening in the frame.
Motors on the other hand , have to be installed right in the place of use which may have dust, dampness,
inflammable gases, chemical fumes etc . To protect the motors against these elements , the motor frames are made
either partly closed or totally closed or flame proof etc.
- How will you change the direction of rotation of a d.c motor?
Either the direction of the main field or the direction of current through the armature conductors is to be reserved.
- What is back emf in d.c motors ?
As the motor armature rotates , the system of conductor come across alternate North and South pole magnetic fields causing an emf induced in the conductors. The direction of the emf induced in the conductors . The direction of the emf induced is in the direction opposite to the current .As this emf always opposes the flow of current in motor operation it is called back emf.
- Under what condition the mechanical power developed in a dc motor will be maximum?
Condition for mechanical power developed to be maximum is
Eb = Ua /2
or I a= Ua / 2Ra
- What is the function of a no-voltage release coil provided in a dc motor starter?
As long as the supply voltage is on healthy condition the current through the NVR coil produce enough magnetic
force of attraction and retain the starter handle in the ON position against spring force. When the supply voltage fails or becomes lower than a prescribed value the electromagnet may not have enough force and the handle will come back to OFF position due to spring force automatically. Thus a no-voltage or under voltage protections given to the motor.
- Enumerate the factors on which the speed of a dc motor depends.
N = 1/CE (Ua-IaRm)/ф
The speed of dc motor depends on three factors.
- Flux in the air gap
- Resistance of the armature circuit
- Voltage applied to the armature
- List the different methods of speed control employed for dc series motor
- Field diverter method
- Regrouping of field coild\s
- Tapped field control
- Armature resistance control
- Armature voltage control for single motor
- Series parallel control for multiple identical motors
- Draw the N Vs Eb characteristics of a dc motor for two different field currents.
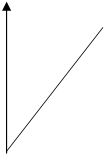
 If<Ifn
If<Ifn
 Nn
Nn
 Ifn
Ifn

Ehn
45.What are the principal advantages of rotating field system type of construction of synchronous machines?
- Form Stationary connection between external circuit and system of conditions enable the machine to handle large amount of volt-ampere as high as 500 MVA.
- The relatively small amount of power required for field system can be easily supplied to the rotating field system via slip rings and brushes.
- More space is available in the stator part of the machine for providing more insulation to the system of conductors.
- Insulation to stationary system of conductors is not subjected to mechanical stresses due to centrifugal action.
- Stationary system of conductors can easily be braced to prevent deformation.
- It is easy to provide cooling arrangement.
46. Write down the equation for frequency of emf induced in an alternator.
F = PN / 120 Hertz
Where P = No. Of poles
N = Speed in rpm.
47. What are the advantages of salient pole type of construction used for synchronous machines?
- They allow better ventilation.
- The pole faces are so shaped radial air gap length increases from the pole center to the pole tips so that flux distribution in the air gap is sinusoidal in shape which will help to generate sinusoidal emf.
- Due the variable reluctance, the machine develops additional reluctance power, which is independent of excitation.
48. Why do cylindrical rotor alternators operate with steam turbines?
Steam turbines are found to operate at fairly good efficiency only at high speeds. The high-speed operation of rotor tends to increase mechanical losses, so the rotors should have smooth external surface. Hence smooth cylindrical type rotors with less diameter and large axial length are used for synchronous generators driven by steam turbines with either 2 or 4 poles.
49.Which type of synchronous generators are used in Hydroelectric plants and why?
As the speed of operation is low, for hydro turbines used in hydroelectric plants, salient pole type synchronous generators are used. These allow better ventilation and also have other advantages over smooth cylindrical type rotor
50. What is the relation between electrical degree and mechanical degree?
Electrical degree θe and mechanical degree are related to one another by the number of poles P, the electrical machine has, as given by the following equation.
θe = (P/2)
51. What is the meaning of electrical degree?
Electrical degree is used to account the angle between two points in rotating electrical machines. Since all electrical machines operate with the help of magnetic fields, the electrical degree is accounted with reference to the polarity of magnetic fields. 180 electrical degrees is accounted as the angle between adjacent North and South poles
52. Why short-pitch winding is preferred over full pitch winding?
Advantages: -
- Waveform of the emf can be approximately made to a sine wave and distorting harmonics can be reduced or totally eliminated.
- Conductor material, copper is saved in the back and front-end connections due to less coil span.
- Fractional slot winding with fractional number of slots/phase can be used which in turn reduces the tooth ripples.
- Mechanical strength of the coil is increased.
53. Write down the formula for distribution factor.
Kd = sin (mβ/2) or Kdn = sin (mnβ/2)
msin(β/2) msin(nβ/2)
where
m - number of slots/pole/phase
β - angle between adjacent slots in electrical degree
n - order of harmonics.
54. Define winding factor.
The winding factor Kw is defined as the ratio of phasor addition of emf induced in all the coils belonging to each phase winding of their arithmetic addition.
55. Why are alternators rated in kVA and not in kW?
The continuous power rating of any machine is generally defined as the power the machine or apparatus can deliver for a continuous period so that the losses incurred in the machine gives rise to a steady temperature rise not exceeding the limit prescribed by the insulation class. Apart from the constant loss the variable loss incurred in alternators is the copper loss, occurring in the 3-phase winding, which depends on I2R, the square of the current delivered by the generator. As the current is directly related to apparent power delivered by the generator, the alternators have only their apparent power in VA/kVA/MVA as their power rating.
29. 56. What are the causes of changes in voltage of alternators when loaded?
- Voltage variation due to the resistance of the winding R.
- Voltage variation due to the leakage reactance of the winding X1.
- Voltage variation due to the armature reaction.
30. 57. What is meant by armature reaction in alternators?
The interaction between flux set up by the current carrying armature conductors and the main field flux is defined as the armature reaction.
31. 58. What do you mean by synchronous reactance?
It is the sum of the leakage reactance X1 and armature reactance Xa
Xs = X1 + Xa
- 59. What is synchronous impedance?
- The complex addition of resistance R and synchronous reactance jXs is synchronous impedance Zs. = (R+jXs)= Zs∟θ
Where θ = tan –1(Xs/R)
|Zs| = √(R2+jXs2)
33. 60. What is meant by load angle of an alternator?
The phase angle introduced between the induced emf phasor E and terminal voltage phasor V during the load condition of an alternator is called load angle. The load angle increases with increase in load. It is positive during generator operation and negative during motor operation.
34. 61. Define the term voltage regulation of alternator.
It is defined as the change in terminal voltage from no load-to-load condition expressed as a function or terminal voltage at load condition, the speed and excitation conditions remaining same.
% Regulation = (E-V)/V x 100
62. What is the necessity for predetermination of voltage regulation?
Most of the alternators are manufactured with large power rating and large voltage ratings. Conduction load test is not possible for such alternators. Hence other indirect methods of testing are used and the performance can be predetermined at any desired load currents and power factors.
63. Why is the synchronous impedance method of estimating voltage regulation is considered as pessimistic method?
Compared to other methods, the value of voltage regulation obtained by this method is always higher than the actual value and therefore is called pessimistic method.
64. Why is the MMF method of estimating the voltage regulation is considered as the optimization method?
Compared to EMF method, MMF method involves more number of complex calculation steps. Further the OCC is referred twice and SCC is referred once while predetermining the voltage regulation for each load condition. Reference of OCC takes core saturation effect. As this method requires more effort, the final result is very close to the actual value. Hence this method is called the optimistic method.
65 .What are the two types of 3-phase induction motor?
- Squirrel cage induction motor.
- Slip ring induction motor.
46. 66. Write the two extra features of slip ring induction motors.
- Rotor is having 3-phase winding.
- Extra resistance can be added in the rotor circuit for improving in the power factor with the help of three slip rings.
67.Can we add extra resistance in series with squirrel cage rotor? State the reason?
We cannot add extra resistance in series with the rotor because all the copper bars of the rotor are short circuited in both the sides by copper end rings to have a closed circuit.
68.Why an induction motor is called rotating transformer?
The rotor receives electrical power in exactly the same way as the secondary of a two winding transformer receiving its power from primary. That is why an induction motor can be called as a rotating transformer i.e., in which primary winding is stationary but the secondary is free to rotate.
69.Why an induction motor will never run at its synchronous speed?
If it runs at synchronous speed then there would be no related speed between the two, hence no rotor emf, no rotor current so no rotor torques to maintain rotation. That is why the rotor runs at its synchronous speed.
70.What are slip rings?
The slip rings are made of copper alloys and are fixed around the shaft insulating it. Through these slip rings and brushes the rotor winding can be connected to external circuits.
71.State the difference between slip ring rotor and cage rotor of an induction motor?
Slip ring rotor has 3-phase windings. Three ends of which are stared and the other three ends are brought up and connected to 3 slip rings mounted in the shaft. Extra resistance can be added in the rotor circuit. Squirrel cage rotor has short-circuited copper bars. Extra resistance can’t be added as slip ring rotor.
72.Write an expression for the slip of an induction motor.
Percentage slip = (Ns -Nr) / Ns * 100.
73.Define slip of induction motor?
Slip is descriptive of the way in which the rotor slips back from synchronism. It is usually expressed as
percentage of synchronous speed.
74.What is cogging of an induction motor?
When the number of stator and rotor teeth’s is equal they have a tendency to align themselves exactly to minimum
reluctance position. Thus the rotor may refuse to accelerate. This phenomenon is known as cogging.
75.What are the advantages of cage motor?
- Since the rotor has very low resistance, the copper loss is low and efficiency is high
On the account of simple construction of rotor, it is mechanically robust.
- Initial cost is less.
- Maintenance cost is less.
- Simple stating arrangement
76.Give the condition for maximum torque for 3-phase induction motor?
The rotor resistance and rotor reactance should be equal for developing maximum torque i.e. R2 = s X2 where s is the slip.
77. What is reason for inserting additional resistance in rotor circuit of a slip ring induction motor?
Introduction of additional resistance in the rotor circuit will increase the starting torque as well as running torque. Also it limits the starting current.
78. List out the methods of speed control of cage type 3-phase induction motor?
a) By changing supply frequency
b) By changing the number of poles
c) By operating two motors in cascade
79.Mention different types of speed control of slip ring induction motor?
- By changing supply frequency
- By changing the number of stator poles
- By rotor rheostat control
- By operating two motors in cascade
60.What are 80. What are the advantages of 3-phase induction motor?
- It was very simple and extremely rugged, almost unbreakable construction
- Its cost is very low and it is very reliable
- It has been suffiently high efficiency .No brushes are needed and hence frictional losses are reduced
- It requires minimum of maintenance.
61. 81. What is meant by crawling of induction motor?
Squirrel cage type, sometimes exhibit a tendency to run stably at speeds as low as 1/7 the of their synchronous speed this
phenomenon is known as crawling
62 . 82. State the application of an induction generator?
- Used in windmill for generating electric power.
- Used in regenerative breaking places like traction.
Source : http://www.niceindia.com/qbank/Electrical_Engineering.doc
Web site link to visit: http://www.niceindia.com
Google key word : Electrical engineering technology file type : doc
Author : not indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly.
Electrical engineering technology
If you want to quickly find the pages about a particular topic as Electrical engineering technology use the following search engine:
Electrical engineering technology
Please visit our home page
Larapedia.com Terms of service and privacy page