FMEA Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
FMEA Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
The following texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
FMEA Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
FMEA Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
Failure modes and effect analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach to: 1) identifying the ways in which a process can fail to meet critical customer requirements, 2) estimating the risk of specific causes with regard to these failures, 3) evaluating the current control plan for preventing these failures from occurring, and 4) prioritizing the actions that should be taken to improve the process. FMEA is a disciplined procedure that allows the engineer to anticipate failures and prevent their occurrence in manufacturing. The concept of FMEA is to identify ways the product or process can fail, and then plan to prevent those failures.
There are essentially three types of FMEA. They are:
System FMEA: is used to analyze systems and subsystems in the early concept and design stages. This type focuses on potential failure modes associated with the functions of a system caused by design.
Design FMEA: is used to analyze products before they are released to production.
Process FMEA: is used to analyze manufacturing and assembly processes.
The two key terms in the title are effects and failure mode. An effect generally refers to the impact on customer requirements. Normally an external customer focus is employed (a failed product under warranty), but the focus can also include downstream processes (internal customers). A failure mode is the way in which a specific process step (input) fails (if not detected and either corrected or removed). When this occurs, a failure mode will cause one of the effects to occur. A failure mode can sometimes be identical to effect, and can be associated with a defect or a process input variable that goes "out of specification". Figure 32.3 illustrates some typical types of effects and failure mode relationships. The key here is that within the FMEA, the cause of the situation (effect) must be related to specific process activities so that the effect can be eliminated.
Several tools are used to help in FMEA. Perhaps that must common tool is a fishbone diagram. Figure 32.4 shows a typical Fishbone diagram. The key to using a Fishbone diagram is to understand how the product relates to its components, and then how to relate the effect back to a particular cause so that a control action can be taken.
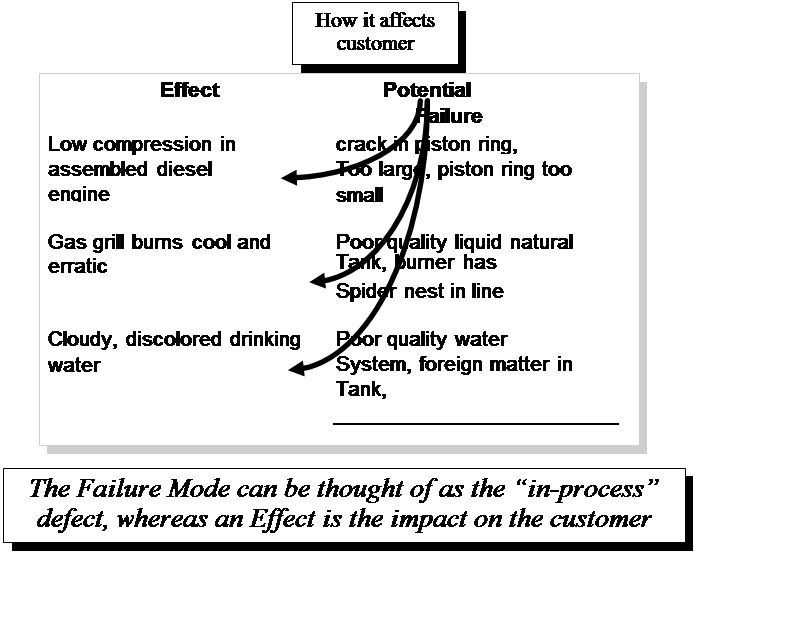
Figure 32.3 Illustration of Failure modes and effects.
Source : http://www.ise.ncsu.edu/wysk/pictures/CHAPTER%2032.doc
Web site link to visit: http://www.ise.ncsu.edu
Google key word : FMEA Failure Modes and Effects Analysis file type : doc
Author : not indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly.
FMEA Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
If you want to quickly find the pages about a particular topic as FMEA Failure Modes and Effects Analysis use the following search engine:
FMEA Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
Please visit our home page
Larapedia.com Terms of service and privacy page