History of religions summary and study guide
History of religions summary and study guide
The following texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
History of religions summary and study guide
Religions
Franceschini
Common Core SS Standards addressed throughout the reading packet:
6H.2.2 Compare historical and contemporary events and issues to understand continuity and change.
6H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne and Qin Shi Huangdi
6C&G.1.2 Summarize the ideas that shaped political thought in various civilizations, societies and regions (e.g., divine right, equality, liberty citizen participation and integration of religious principles).
6C&G.1.4 Compare the role (e.g., maintain order and enforce societal values and beliefs) and evolution of laws and legal systems (e.g., need for and changing nature of codified system of laws and punishment) in various civilizations, societies and regions.
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
6C.1.3 Summarize systems of social structure within various civilizations and societies over time (e.g., Roman class structure, Indian caste system and feudal, matrilineal and patrilineal societies).
Common Core Reading Standards addressed throughout the reading packet:
- Locate and cite details, State main ideas and summarize.
- Determine meanings of words and phrases.
- Determine how information is presented (sequentially, comparatively, etc.).
- Integrate and analyze visuals (maps, charts, pictures) etc. with text.
Common Core Writing Standards addressed throughout the reading packet:
- Produce clear and coherent writing appropriate for the task.
- Use technology and internet to produce writing.
- Informative and Explanatory Writing in the context of SS
Unit Vocabulary:
Students should write the bold faced words in their vocabulary journal. They should write a definition and write the sentence as used in context. When possible, a picture, symbol or icon should accompany each
Hinduism
Hinduism-Introduction
Objectives: SWBAT explain how Hiduism began. SWBAT contrast Hinduism with the major monotheistic religions.
6H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne and Qin Shi Huangdi
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
6C.1.3 Summarize systems of social structure within various civilizations and societies over time (e.g., Roman class structure, Indian caste system and feudal, matrilineal and patrilineal societies).
Hinduism began over 5,000 years ago. It is the world’s oldest religion. About 80% of all Indians are Hindu. Hinduism was not founded (started) by just one person. It began with the Harappan civilization of India and evolved(changed) over thousands of years with the Aryans. Hinduism also does not just follow one book. It has a collection of prayers and readings called the Vedas. It also has a collection of hymns (religious songs) called Upanishads. The Vedas and Upanishads act as a guide to the Hindu religion.
Hinduism is very different than Judaism, Christianity and Islam. First, both Christianity and Islam worship one God whereas Hinduism worships thousands of gods. Hindus are allowed to choose their favorite god. Second, both Christianity and Islam have only one book, the Bible for Christianity and the Koran for Islam. However, the Vedas are a collection of many separate readings. Lastly, both Christianity and Islam have one founder, Jesus for Christianity and Muhammad for Islam. Hinduism does not have one person who began it. It began with the ancient Harappan culture and evolved over thousands of years.
Essential Questions:
- How old is Hinduism?
- Why are the Vedas and Upanishads important?
- Name the three ways Hinduism is much different from both Christianity and Islam. Hindu temple in india
Four Important Aspects of Hinduism
Objectives: SWBAT explain and summarize the aspects of Hinduism.
Aspect 1
There are four very important aspects to the Hindu religion. The first important belief of Hinduism is that there is one Great Spirit in the universe, which is the creator of all life. This spirit is called Brahman. However, this spirit can appear as many different gods so the Hindus worship thousands of gods. Vishnuis one god. Vishnu is the preserver of all life (in other words Vishnu keeps everyone and every thing alive). Shivais another god. Shiva is the destroyer of all life. These are just two examples of Hindu gods out of thousands. All of these gods together make up Brahman.
Essential Questions:
- What is the first important aspect of Hinduism?
- What is Brahman?
Aspect 2
Hindus believe all life is sacred and all living things have souls. Our soul is like a ghost that lives inside us. A soul never dies. After a body dies the soul looks for a new body to live in. This brings us to the second important Hindu belief called reincarnation. Reincarnationis the Hindu belief that after someone or something dies its soul goes to live in a new body. In other words the soul comes back to life in a new body. It could be the body of a person, an insect, an animal or whatever else that lives. To a Hindu, a spider has a soul just like a person does. One holy animal is the cow. Hindus will not harm or eat a cow.
Questions:
- What are the first two important Hindu beliefs?
- What is reincarnation?
Aspect 3
A third important belief of Hinduism is Karma. Karmais the belief that a person’s behavior in life will affect how the soul gets reincarnated. If a person behaves well during his or her life then they will come back to life as someone or something better than before. For example, a person who was a slave might be reincarnated as a farmer. If a person behaves badly during his or her life then they might come back as someone or something lower. For example a person could be reincarnated as a rat or a snake. You are punished for bad things done in your previous life.
Essential Questions:
- What is Karma?
- What might happen if a poor person leads an excellent life? In other words, what might they come back as? What would happen if they behaved poorly?
Aspect 4
The fourth important aspect of Hinduism is the goal to reach nirvana. Nirvanais when a soul becomes part of the Great Spirit – Brahman. The goal of every Hindu is to eventually stop the reincarnation cycle of life and just be part of Brahman. This is not an easy task. It takes many lifetimes for the well behaved. Poorly behaved may never reach nirvana.
Essential Questions:
- What is nirvana?
- What are the four important aspects of Hinduism?
- What is the goal of every Hindu?
The Caste System
Objectives: SWBAT ID the different castes. SWBAT evaluate the role of reincarnation in the caste system.
The ancient Aryans put all people into groups. Each group was called a caste. Castes are social groups that rank people into high positions in society and low positions in society. The caste system became part of the Hindu religion long ago. In ancient India there were four main castes. These castes from most important to least important were the Brahmins (priests), the Kshatriyas (kings and warriors), the Vaishyas (landowners and businessmen) and the Sudras (workers- peasants and slaves). Another group of people was totally out of the caste system. These people were called the Untouchables or Outcastes. These people were considered so low in society that no one from the other castes would go near them, talk to them or touch them. They had to do the worst jobs like picking up garbage and cleaning sewers.
Clothes are a symbol of caste
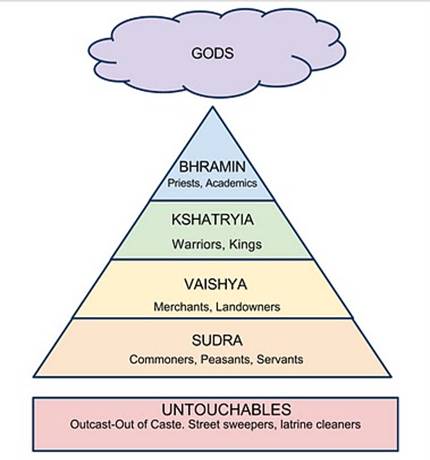
People were born into a caste. You could not move up to another caste or move down to another caste. For example if you were born into the warrior caste you could not move up to the Brahmin caste. The only way to change castes was through reincarnation. Remember that this is the belief that your soul is born again into another body after you die. The Hindus believe that if you live your life as a good person you will be born into a higher caste in your next life. If you live your life as a bad person then you will be born into a lower caste or even an animal or insect.
The four major castes are also divided into smaller castes called jatis. For example within the businessman caste there are many jatis. For example a shoemaker is one jati and a tailor is another jati. A person could not marry or socialize with a person from another caste. For example someone from the peasant worker caste could not marry a person from the warrior caste. The clothes people wore showed their caste and jati.
Essential Questions:
- Who began the caste system?
- What are the four main castes?
- Which group of people was considered so low that they were not even a caste?
- What role does reincarnation play?
The Caste System Today
Hinduism is both a religion and as social system. The caste system determines where you are in society and the people who you should be with. The castes in which people are born into affect their jobs, friends, and people they marry. You cannot marry outside your caste. However, within the last 50 years some Hindus have tried to change the caste system because many people feel it is unfair. Mohandas Gandhi was the leader of India in the 1930’s. He was one of the first leaders to speak against the caste system. He especially did not like the way the untouchables were treated. By 1950 the government of India passed a law that forbids (not allow) discrimination against people from the lower castes. Discrimination means treating people unfairly because of the color of their skin or because of their position in society. This was especially done to help the untouchables because many Indians treated them very badly.
Even though laws have been passed there is still a lot of discrimination against lower castes. In the big cities there is less discrimination but in the small villages there is still a lot of discrimination against the untouchables. For example the untouchables must drink from different wells and use different bathrooms. Just because a government passes a law it does not make everything perfect right away. Hinduism and the caste system have been around for thousands of years. It often takes a long time to change people’s feelings and beliefs.
Essential Questions:
- Why do many Indians want to change the caste system?
- Who was Gandhi? Why was he important?
- When did the Indian government end discrimination based on caste? Who did this help the most?
- Why is there still a lot of discrimination against lower castes today?
- In what way was segregation of African Americans similar to practices against the Untouchables of India?
Buddhism
Introduction
Objectives: SWBAT explain the significance of Siddhartha Gautama. SDWBAT interpret the 4 Noble Truths and the 8 Fold Path. SWBAT argue ad justfy opinions about Buddhist philosophy of life.
6H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne and Qin Shi Huangdi
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
India was also the birthplace of another great world religion, Buddhism. This religion began about 500 BC. It began with a man called Buddha. He did not believe in the Hindu Gods. Buddha also did not like the caste system. He felt many of the people were not treated fairly. He felt that all people were equal and that everyone must be treated equally. Buddha taught that people should be good to one another. Many Indians liked what Buddha was teaching. The people who began following Buddha were called Buddhists. Although there are Buddhists in India, Hinduism was and still is still the predominantreligion in India. Predominant means what most people do or want. About 83% of the people of India are Hindus. Buddhism spread to China and other South and Southeast Asian countries and made its largest impact in these regions.
Buddhism Part 1
Buddhism actually began in India but most of the people of India remained Hindus. However, Buddhism did spread to both East Asia and Southeast Asia and became the predominant (most popular) religion.
A prince from Nepal named Siddhartha Gautama began Buddhism. He began his religion around 500BC. He was a very rich man. He wanted to know why there was so much suffering and pain in the world. Why couldn’t everyone be happy? One day he had a vision. He became very concerned about the poor. He then gave up all of his wealth and began to spread his new beliefs. He then changed his name to Buddha, which means the enlightened one or in other words, the one who knows everything.
Essential Question:
- Who was Siddhartha Gautama and why was he important?
Complete each sentence:
- Siddhartha Gautama changed his name to ____________
- Buddhism actually began in ____________________.
- Siddhartha Gautama wanted to know why there was so much ______________ and _______________ in the world.
Buddhism Part 2
Buddhism is a bit different than other religions. It does not have a belief in a supreme god. Buddhism accepts the Hindu beliefs of Karma and reincarnation, but it rejects the caste system. Buddha was concerned with all human suffering. He did not like the caste system because it kept people in bad situations.
Buddha based his religion on four basic beliefs. He called these the Four Noble Truths:
- Our lives are full of pain and suffering.
- Our pain and suffering are caused by our desire to have things.
- We need to get rid of our desire to have things in order to end our pain and suffering.
- We must follow the eight-fold path in order to end our desire to have things. (see next reading for eight-fold path)
Basically what Buddhism teaches is that living as human beings is very painful for our bodies, minds and souls. People are reincarnated many times into this terrible world. People suffer because they want to own and control too many things. In order to end this pain and suffering a person needs to stop wanting to own and control things. For example, many people want nice cars. But Buddha feels that wanting a car and then having a car will never make a person happy forever.
Essential Question:
- What do the 4 Noble Truths do?
Complete each sentence:
- Buddhism accepts the Hindu beliefs of _______________ and reincarnation.
- Buddhism rejects the Hind belief in the ____________ system
- Karma refers to a how a person’s behavior in this life will affect their next __________.
- In Hinduism, the _____________ system puts people into different social groups in which they cannot ever move out of during their life.
- ___________ is the Hindu belief of the soul getting reborn into another body
Buddhism Part 3
Buddhists feel a person must end their desire to own things for themselves. To do this a person must follow The Eight-Fold Path. These are eight things all people must do in order to end their desire to own material things. If a person follows this path then he/she can end all desire to want things. These are the eight things:
- talk correctly
- act correctly
- see things correctly
- have good intentions
- be good at your work
- always try your hardest
- concentrate hard on all things you do
- always think about what you do
If a person follows these eight steps in life then a person will reach nirvana. Nirvana is the perfect state of happiness where a person does not have any desires. The only thing that matters is happiness. To be happy, a person needs nothing. Once a person reaches nirvana then they never need to be reborn again. The cycle of reincarnation can end (this is very similar to the Hindu belief).
Buddhism spread quickly amongst the poor people because it offered people a way to be happy forever even though they had nothing. Today there are over 300 million people who follow Buddhism, most of whom live in East Asia and Southeast Asia.
Essential Question:
- What is the ultimate goal for a Buddhist by following the Eight Fold Path?
- Why do you think Buddhism appeals to the poor?
Activity:
- Create posters that summarize and highlight the 4 Noble Truths and the 8 Fold Path
Argumentative Writing Prompt:
- Do you agree or disagree with the ideas of Buddhism. Consider and analyze the Four Noble Truths, the Eight Fold Path and the idea of Nirvanna.
- You should have the following in your essay:
- Introduction- Summarize what Buddhism is and given your opinion.
- Body – Support your opinion and argument with details.
- Conclusion- Restate the main ideas using different words and expressions
Confucianism
Objectives: SWBAT ID who Confucius was and retell the main idea of Confucianism
6H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne and Qin Shi Huangdi
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
In ancient China around 2,500 years ago there was a great teacher by the name of Confucius. He lived during the late Chou Dynasty. He was very important because he set a guideline of morals and values that all Chinese people were to live by. Morals and values refer to how a person is supposed to behave in society. Sometimes we call them ethics. These ethical beliefs became part of Chinese society and culture for thousands of years. Today the Chinese still believe in his teachings.
Confucianism is not a religion. It is a philosophy. What is the difference between a religion and a philosophy? Religions refer to a belief in a god or many gods. Philosophy just refers to what people believe to be correct or true. For example, the belief that all people are created equal is a philosophy not a religion. Confucius felt that China was a large family and that the emperor was like a father. To Confucius, the family was the most important thing in society. The family taught correct behavior and loyalty. The father was the head of the family. He was responsible for teaching morals and values to the family and setting a good example. He did this by learning as much as he could, being kind, being honest and being helpful toward others. The emperor, just like the father was to do all these things for the people of his nation. Confucius felt that all humans were good and that if everyone followed these beliefs then there would be a perfect society. People became bad when they did not follow these guidelines and beliefs. Confucianism believed that the whole society was more important than any one individual person was.
Confucius
Essential Questions:
- Who was Confucius and why was he important?
- What is the difference between a religion and a philosophy? Why is Confucianism considered a philosophy?
- What did Confucius believe was the most important thing in society?
- According to Confucius, how could there be a perfect society?
Taoism
Objectives: SWBAT contrast the beliefs o Taoism with Confucianism.
6H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne and Qin Shi Huangdi
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
A contemporary to Confucius was a teacher named Laozi. He created another philosophy or belief system of the Chou Period was Taoism (Daoism). Many of the beliefs of Taoism are the opposite of Confucianism. Unlike Confucianism, Taoism taught that the individual was more important than the family. The most important thing was not good government, but rather, the most important thing for people was nature. People needed to respect nature and live in harmony with it. Taoists believe that people should not try to change things through government because no matter how hard you try a person cannot change nature. Rather than trying to control nature people need to accept nature and live with it. In other words people should just accept whatever happens in life. This is very different from Confucianism which taught people to believe that a person must learn as much as possible in order to control things in life.
Many Chinese people believed in both of these teachings and took a little bit from each one. Many Chinese practiced both Confucianism and Daoism. Confucianism taught them how to behave towards one another, while Daoism taught them how to behave towards the natural world and with themselves personally.
Essential Question:
- How does Taoism differ from Confucianism?
Other Questions:
- What is the most important thing in society to a person who follows Confucius? What is the most important to a Daoist?
- Why do Daoists believe trying to change things through government is not a good idea?
- Which philosophy do you like better? Why?
Southwest Asia/The Middle East
A Region of Religion
Objectives- SWILLBAT explain the difference between monotheism and polytheism.
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
As we have already discussed, both Mesopotamia and Phoenicia were the sites (place) of some of the earliest civilizations. These early civilizations had religions where people believed in many gods. The belief in many gods is called polytheism. Each city-state worshipped different gods.
The Middle East is not only important for these great civilizations but also because it was the place where three of the world’s greatest religions began. These three religions would not be based on polytheism. These three religions would be based on monotheism. Monotheism is the belief in only one god. The three great religions that began in the Middle East are Judaism, Christianity and Islam.
Essential Questions:
- What is the difference between monotheism and polytheism?
- What are the three great monotheistic religions?
Assignment: Write 5 questions and answers. Your questions must be information questions. They must begin with a “Wh” word (who, what, when, where, how, why or which)
Judaism
Objectives- SWILLBAT state what made the Hebrew people and their religion of Judaism significant.
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
6H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne and Qin Shi Huangdi
6C.1.3 Summarize systems of social structure within various civilizations and societies over time (e.g., Roman class structure, Indian caste system and feudal, matrilineal and patrilineal societies).
The first great religion was Judaism. Judaism was the religion begun by the Hebrew people around 2000 BC. The Hebrew people were originally from Sumer but eventually they moved to the land called Canaan on the Jordan River. Today Canaan is the country of Israel. Judaism is a 4,000-year-old religion. The Hebrews worshipped a single God called Yahweh. Jews believe God chose them to be an example for the world. The Torah is the holy book of the Jewish religion (Christians call it the Old Testament). Because there was little water in Canaan, the Hebrew people often went to parts of Egypt to live. The pharaohs (kings) of Egypt did not like the Hebrews because of their religion—Judaism. The Egyptians made many of the Hebrew people into their slaves.
Around 1230 BC a leader named Moses led the Jews out of Egypt back to Canaan. Moses also gave the Hebrews the Ten Commandments. The Ten Commandments were the holy laws that the Jewish people were to live by. For example people were not allowed to steal, fight, kill, lie or cheat. In Canaan the Jewish people built the powerful Kingdom of Israel led by powerful kings like Saul, David and Solomon. These kings built the first temples. Temples were giant buildings where the people would worship.
By about 600 B.C. the Kingdom of Israel was destroyed by the Persians. For the next 700 hundred years or so the Jews of Canaan were ruled by different nations such as the Persians, Greeks, Syrians and finally the Romans. These civilizations did not like the Hebrew people and their religion because the Jews only worshipped one God. The Romans especially did not like the Jews of Cannan. The Romans were still polytheistic. They worshipped many gods. By 70 AD, the Roman army destroyed the Jewish holy city of Jereselum. The Jews were forced out of Cannan. Many of the Hebrew people had to move to other parts of the world. The movement away from Cannan to other parts of the world was called Diaspora. This is how many Jewish people ended up living in European countries.
Essential Question:
- Why were the Hebrew people and their religion of Judaism so significant?
Assignment: Write 7 questions and answers. Your questions must be information questions. They must begin with a “Wh” word (who, what, when, where, how, why or which)
Additional Questions:
- What is the difference between these two words—“Judaism” and “Hebrew”?
- What were Israel and Palestine originally called?
- Who was Moses and why was he so important?
- Why do you think many Jewish people went to Europe to live?
Christianity
Objectives- SWILLBAT identify and list the main principles of Christianity. SWILLBAT compare & contrast using Venn Diagrams the differences in what Jews believe and what Christians believe.
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
6H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne and Qin Shi Huangdi
Christianity began 2,000 years ago with the teachings of Jesus and his followers. Christianity developed from Judaism. During this time the Romans were persecuting Jews. Persecute means to treat very badly or even kill. In order to survive some Jews tried to change and live with the Romans. Other Jews became angry and tried to kill Romans. And finally some Jews moved away from civilization into the mountains and wilderness. In the wilderness, the Jews hoped to be left alone. They waited for the Messiah. The Messiah would be a messenger from God that would help the Jews rebuild the Kingdom of Israel.
This is the world Jesus was born into. Jesus and his followers were Jews. Jesus felt that many Jews were not living the correct way. Many Jews were not following the Torah. Jesus felt many of his Jews were sinners. A sinner was anyone who did not live by the word of God as said in the Torah. He felt there was too much greed, selfishness and hatred. Jesus went from town to town and taught that all people must love one another and help one another. Only then would God help people. Some Hebrews began to follow Jesus. Many other non-Jews also began to follow Jesus because he promised salvation. Salvation means being saved and forgiven by God for sins. In other words, all people could go to heaven as long as they believed in God and Jesus Christ’s teachings. Some of the Jews began to believe Jesus was the Messiah. They came out of hiding and began following Jesus. His twelve original followers were called the disciples or apostles. They helped him spread his word. Soon many people were following Jesus and his teachings.
However, there were many other Jews who did not believe Jesus and did not believe he was the Messiah. Many Jewish religious men thought that Jesus was trying to take away their power by telling lies. The Romans did not like Jesus as well. The Romans had their own gods. They saw Jesus as a threat to their rule in Israel. The Romans crucified Jesus. Crucify means to hang and kill someone on a cross.
Christians believe that Jesus was the Son of God. They believe Jesus was sent by God as a Messiah or messenger of God. The Christians believed that after Jesus was crucified he rose into heaven with God. The rising into heaven is known as the resurrection.
After Jesus was crucified many of his followers continued his teachings. For many years the Christians were put to death by the Romans but eventually most of the Roman people would also convert (change) to Christianity. The Christian Bible is made up of the Old Testament, including the Ten Commandments and the New Testament. The Old Testament is the original teachings of Judaism. Christians accept the Old Testament, but also believe in the New Testament. The New Testament contains the story of Jesus and his teachings. Judaism rejects the New Testament. The Jewish people do not believe that Jesus was the Son of God and the messiah, while the Christians do.
Essential Question:
- How and when did Christianity begin?
- What do all Christians believe?
- What are the similarities and differences in what Jews and Christians believe. Draw a Venn Diagram.
Assignment: Write 10 questions and answers. Your questions must be information questions. They must begin with a “Wh” word (who, what, when, where, how, why or which)
Islam
Objectives- SWILLBAT explain the significance of Muhammad and his teachings. SWILLBAT explain why Muslims believe Muhammad was different than previous prophets.
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
6H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne and Qin Shi Huangdi
Islam is the third great religion to come from the Middle East. Just like Judaism influenced Christianity, Judaism and Christianity also influenced Islam. Islam is a monotheistic religion that means, “surrender to God’s will”. Today most people of the Middle East and North Africa follow Islam. They are Muslims. Muslims are the people who follow Islam. It is the fastest growing religion in the world today
The founder of Islam was a man named Muhammad. He was born around 570 A.D. He lived in Mecca in present-day Saudi Arabia. The people of Mecca and Arabia worshipped hundreds of gods. Muhammad did not believe in all of these gods. When he was about 40 years old, Muhammad began to have visions (dreams). He came to believe there was only one God whom he called Allah. Muhammad continued to have these visions. He believed these visions were given directly to him by Allah. He believed Allah gave him these visions so he could teach other people about these revelations (messages from God/Allah). Muhammad said he was sent by Allah as his prophet. A prophet is a messenger of God.
Muhammad's message says there is only God. Allah is all-powerful but also merciful. Muhammad believed there were other prophets in the past who told this same message. Abraham, Moses and Jesus were also prophets who delivered this same message. Allah was the same God both Judaism and Christianity worshipped. Muhammad accepted parts of both the Torah and New Testament as the word of God. However, according to Muhammad, Allah made him the last great prophet. In other words, there would be no more messages from God. Muhammad was his last and greatest prophet.
At first the people of Mecca did not like Muhammad and his teachings about one God. In 622 there is a plan to kill him. Before they could kill him, he escaped from the city. Muhammad then went to the city of Medina. Mohammad’s escape from Mecca to Medina is called the hijra. Muhammad preached his new religion to the people of Medina and soon had many followers. In 630 Muhammad returned to Mecca with an army and captured the city. He made Islam the official religion and declared Mecca to be the holy city of the Islamic religion.
Essential Questions:
- Who was Muhammad?
- What was Muhammad’s message?
- Why do Muslims believe Muhammad was different from other prophets?
Assignment: Write 10 questions and answers. Your questions must be information questions. They must begin with a “Wh” word (who, what, when, where, how, why or which)
Islam After Muhammad- I
Objectives- SWILLBAT ID & explain the 5 Pillars by creating posters.
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
Muhammad died in 632. Soon after his death, some of his followers began writing down his teachings in a book. The book was called the Koran. The Koran was and still is the holy book of Islam. Islam spread like wildfire (very quickly) throughout the Middle East. Muslim armies spread Islam across North Africa, India and even into Spain.
The followers of Islam are called Muslims. Although Muslims accept much of what the Old Testament and the New Testament say, they must follow the words of the Koran. The basic duties of all Muslims are given in the Koran. These basic duties are known as the Five Pillars of Islam. The Five Pillars are things all Muslims must do to be accepted by Allah. Here is a list of the Five Pillars that all Muslims must accept:
- Faith >Allah is the only God and Muhammad is his most important prophet.
- Prayer > Muslims must pray five times a day while facing the city of Mecca.
- Charity/Alms Giving > Muslims must give money to the poor and help the poor. This is called alms giving.
- Fasting > Muslims must fast from sun up to sun down during the month of Ramadan (the 9th month on the Muslim calendar). To fast means not to eat. In other words, during Ramadan Muslims can only eat at night.
- Pilgrimage > Muslims must try and make a trip to Mecca at least once in their life. This trip to Mecca is called the hajj.
Essential Question:
- What are the 5 pillars of Islam?
Assignment: Write 7 questions and answers. Your questions must be information questions. They must begin with a “Wh” word (who, what, when, where, how, why or which)
Activity- Make poster boards showing the Five Pillars if Islam.
Islam After Muhammad- II
Objectives- SWILLBAT explain how Islam united the tribes of the Mideast. SWILLBAT explain how the original caliphs were tolerant toward others.
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
6H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne and Qin Shi Huangdi
Before Muhammad and Islam, most Arab people were living in small groups or tribes throughout the desert. Most of these groups had little communication with each other. When Muhammad introduced Islam to the Arab people, it began to bring all of these separate groups together. After Muhammad died, his son–in–law Ali took over and continued his teachings. Ali had married Muhammad’s daughter. Within 200 years the Arab people were united under Islam and had a huge empire that included all of the Middle East and North Africa as well. The Arab Empire was ruled by the caliph. The caliph was a leader who claimed to be the successor or follower of Muhammad. He was almost like a king of the empire. After the Arab Empire conquered a region, the Arab people did not force anyone to convert to Islam. They were very tolerant? Tolerant means to allow people to choose things for themselves. Many people simply chose to convert to Islam because they liked it. The caliph however, let people choose to worship any religion they wanted to. Christians and Jews were allowed to practice their own religion.
Essential Question:
- How did Islam unite the Arab tribes?
- How were the original caliphs tolerant toward other people?
Assignment: Write 7 questions and answers. Your questions must be information questions. They must begin with a “Wh” word (who, what, when, where, how, why or which)
Sunni and Shiite
Objectives- SWILLBAT explain the difference between Sunnis and Shiites.
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
6H.2.4 Explain the role that key historical figures and cultural groups had in transforming society (e.g., Mansa Musa, Confucius, Charlemagne and Qin Shi Huangdi
After Muhammad died there was an argument between many of the Muslims about their religion. The argument was about the imams. Imamsare religious leaders. As a result of this argument the Muslims split into two different groups. These two different groups of Islam are called Sunni and Shiite.
The Sunni Muslims believe that the Muslim people should pick the imams. The imam should be a good Muslim as well as have good leadership qualities. The Shiite Muslims believe that imams should only be people who are direct descendants of Mohammed’s daughter or son in law Ali. Descendants are the people of our family who follow us after we die. In other words, the Shiites believe the imams have to be related to Muhammad and Ali. This argument still divides the Muslim people today.About 75% of all Muslims are Sunni. The other 25% are Shiite. The Sunnis disagree with the Shiite belief. They do not feel their leaders must be related to Ali. They feel their leaders should have good leadership qualities.
Essential Question:
- What is the difference between a Sunni Muslim And a Shiite Muslim?
Assignment: Write 7 questions and answers. Your questions must be information questions. They must begin with a “Wh” word (who, what, when, where, how, why or which)
Islam Today
Objectives- SWILLBAT state what Muslims believe today.
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
Muslims believe that Muhammad was God’s last messenger. Even though Christians and Jews did not believe this and still do not believe this, Muhammad taught that all Muslims should respect Christians and Jews.
Islam is more than a religion. It is a way of life. Some Islamic countries, like Saudi Arabia, are stricter than others. Many Muslim countries do not separate government from religion like we do in America. Muslims are not supposed to drink alcohol, gamble or eat pork (because the pig is a holy animal). Islam is a male-dominated society. This means that men are in control of almost everything. Muslim women do not have many rights. For example, in many Muslim countries women are not allowed to drive cars, vote or own property. Men are allowed to have more than one wife but a woman can only have on husband. Women often have to cover their faces with veils. In some countries women are only allowed to work with other women.
Some Muslim countries are more liberal or are getting more liberal. Liberal means allowing more freedoms. Some women are becoming doctors, lawyers and teachers. Turkey is a Muslim country that has more freedom for women.
One of the most important Muslim beliefs is that death in a jihad will guarantee that a person gets into heaven. A jihad is a holy war fought to defend Islam. This belief has been very important throughout history in the Middle East because many Muslims have been willing to die for their religion. They are not afraid to die because it is a safe passage into heaven. Many wars have been fought due to this belief. There have been some Muslims who believe that both Christians and Jews have attacked the Islamic religion. As a result, they also believe a jihad is justified against infidels (non believers who threaten Islam).
It is very important to understand that not all Muslims believe they are threatened. Most feel a jihad is not warranted.
Questions:
- What is the difference between what Muslims believe about Muhammad and what Christians and Jews believe about Muhammad?
- Name two things Muslims are forbidden from doing.
- How are women in the Middle East treated differently than women in America?
- How do you feel about the way women have been traditionally treated in the Middle East? In other words, do you think it is fair? Tell your reason why.
- What is Jihad and why is jihad important?
Summary of the Three Great Religions of the Middle East
Objectives- SWILLBAT compare and contrast the 3 great religions by drawing a chart.
6C.1.2 Explain how religion transformed various societies, civilizations and regions (e.g., beliefs, practices and spread of Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism).
The three great religions have many similarities. All three of the three great religions are monotheistic. All three have millions of followers. All three share some of the same beliefs because Christianity developed from Judaism and Islam developed from both Christianity and Judaism. All three believe in one God. And all three believe that God sent his prophets to speak to the people. A prophet is a messenger sent by God to speak to the people. Christians and Muslims accept many of the same prophets as the Jews. For example, all three recognize Moses and Abraham as great prophets sent by God.
There are also some differences in the great religions. The Jews reject (don’t believe) the Christian belief that Jesus was a prophet or the Son of God. Christians feel that Jesus was the last great prophet of God and the Son of God. The Muslims do believe that Jesus was a prophet, but do not believe he was the last great prophet. The Muslims believe Muhammad was the last prophet sent by God. Both the Jews and Christians reject Muhammad and his teachings. They do not think Muhammad was sent by God. They do not believe Muhammad was sent by God.
Assignment: Make a chart or map that shows how the three religions were both similar and different.
The People of the Middle East- Part I
Objectives- SWILLBAT differentiate between the term Arab and Muslim.
Most people in the Middle East are Arabs. Arabs are people who come from Arabia or descendants of people who originally came from Arabia. Arabia is a peninsula in the Middle East between the Red Sea and Southwest Asia. Today most of it is a country called Saudi Arabia. Over the centuries (a century is 100 years) Arabs have dispersed throughout the rest of the Middle East and North Africa as well. When people of a culture disperse it means that they move away from where they originally lived to many different locations. Because the Arabs moved to all different areas of the Middle East and North Africa, Arabs have often mixed with other groups of people.
Many people confuse the word Arab and Muslim to mean the same thing. They do not mean the same thing! Muslims are people who follow the religion of Islam. It is important to remember that the word “Arab” does not refer to a religion. It refers to the people of Arabia. Most Arabs happen to follow the religion of Islam; therefore they are both Arab and Muslim. However, there are Arabs, who follow different religions. For example, there are some Arabs who believe in Christianity. This makes them Arab Christians. Many of the people in Lebanon are Arab Christians. The opposite could be true as well. There are many Europeans that that believe in Islam. This means they are European Muslims. They are not Arabs.
Essential Questions:
- What is the difference between the terms Arab and Muslim?
- Why do you think people often consider an Arab and Muslim to be the same?
Assignment: Write 7 questions and answers. Your questions must be information questions. They must begin with a “Wh” word (who, what, when, where, how, why or which)
People of the Middle East- Part II
Objectives- SWILLBAT identify and name the different groups of people in the Mideast.
For the most part most of the Middle East speaks Arabic. Arabic is also the religion of Islam. There are also some Muslim people in the Middle East that are not Arabs and do not speak Arabic. Turkey is a Muslim country but most of its people are not Arabs. The Turks speak Turkish and have different customs than their Arab neighbors. Iran is also a Muslim country that is not Arab. The people of Iran are descendants of the people of ancient Persia. They speak a language called Farsi. Iranians also have a different culture than the Arabs. This is part of the reason that Iraq and Iran have been enemies for many years. Even though both countries are Muslim the people of Iraq are Arabic and the people of Iran are Persian. Another Muslim group is the Kurds. They live in the mountains of Iran, Iraq, Syria and Armenia. They have often been persecuted (treated badly) by these countries for their culture and nomadic lifestyle. Nomads are people who do not live in one place. They move from place to place. The Kurds would like to have their own country but none of the countries are willing to give them the land.
Essential Questions:
- What is the language of Islam?
- Which two major countries do not speak Arabic? What languages do they speak?
- Who are the Kurds and where do they live?
- For each of the following use one of the following terms: Arab, Jew, Muslim, Christian, Christianity, Hebrew, Arabic, Farsi, Turkish, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Judaism.
- language spoken in Saudi Arabia-________________
- Official language of Islam-_________________
- Muslim religion-____________________
- Christian religion-__________________
- Jewish religion-_________________
- Language spoken in Iran-________________________
- Main religion in Turkey-___________________
- Main religion in Iran-________________
- Language spoken in Israel-___________________
- Language spoken by the Jews-_____________
- Language spoken by the Arabs-__________________
BB Sentences:
- Hinduism is the religion of India.
- Hindus are people who follow Hinduism.
- Hinduism changed over thousands of years.
- Hinduism does not have just one holy book.
- Hindus worship many gods.
- Hinduism is very different from Christianity and Islam
- Hindus believe in a Great Spirit.
- The Great Spirit is called Brahman.
- Brahman can be many gods.
- Hindus worship thousands of gods.
- Hindus believe all living things have a soul.
- Our soul is like a ghost inside of us.
- All living things have a soul.
- Hindus believe the soul comes back to life after we die.
- Hindus believe good behavior is rewarded.
- Bad behavior is punished.
- Behavior affects reincarnation.
- The ancient Aryans put people into groups.
- A caste is a group of people.
- Hinduism has four castes.
- Priests are the highest caste.
- Peasants were the lowest caste.
- You cannot change castes during your life.
- You can change castes in your next life.
- Hindus believe in reincarnation.
- The caste system has been around for thousands of years.
- The caste system determines your position in society.
- Many people feel the caste system is unfair.
- Gandhi was against the caste system.
- There are laws against discrimination in India today.
- The caste system has been around for thousands of years.
- The caste system determines your position in society.
- Many people feel the caste system is unfair.
- Gandhi was against the caste system.
- There are laws against discrimination in India today.
An example of discrimination in America would be not giving a person a job because he or she is black or Hispanic. In India an example of discrimination would be not giving an untouchable a job because he or she is from a lower caste.
Source : http://franceschini.cmswiki.wikispaces.net/file/view/Religions.doc/405493976/Religions.doc
Web site link to visit: http://franceschini.cmswiki.wikispaces.net
Google key word : History of religions summary and study guide file type : doc
Author : Franceschini or not clearly indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly.
History of religions summary and study guide
If you want to quickly find the pages about a particular topic as History of religions summary and study guide use the following search engine:
History of religions summary and study guide
Please visit our home page
Larapedia.com Terms of service and privacy page