Chemistry notes
Chemistry notes
The following texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
![]()
Chemistry notes
Chemistry
MATTER anything that takes up space and has mass
Made of ELEMENTS -can’t be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions
• 92 naturally occurring elements
• Each has a unique symbol (usually first one or two letters of name)
• Some symbols dervived from Latin EX: Sodium = Na (from Latin natrium)
• 25 chemical elements are essential to life.
• Four elements—carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and nitrogen (N) = 96% of living matter- • Other 4% of organism’s weight = phosphorus (P), sulfur (S), calcium (Ca), and potassium (K)
• TRACE elements =required in minute quantities
- • Some required by all organisms EX: iron (Fe)
- • Others only required by some species
- EX: humans need 0.15 mg Iodine (I) daily for normal thyroid gland function
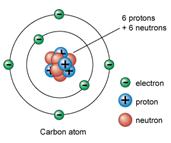 ATOMS made of SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
ATOMS made of SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
Each kind of atom has a specific number of protons, neutrons, and electrons
SUBATOMIC |
Electric charge |
Mass |
Location |
Proton |
+ |
1 dalton |
In nucleus |
Neutron |
_ |
1 dalton |
In nucleus |
Electron |
0 |
negligible |
Orbit nucleus in energy levels |
 Elements in same row have same # of electrons in their outer shells
Elements in same row have same # of electrons in their outer shells
- • As move from left to right, one proton & one electron are
added to preceding element
• Atoms are electrically NEUTRAL (protons =electrons)
• Atoms that have gained or lost electrons = IONS
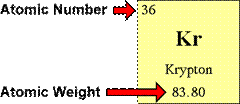
USES OF RADIOACTIVE ISOTOPES : |
= number of protons
= number of protons + neutrons
ATOMIC MASS (1 dalton = 1 amu)
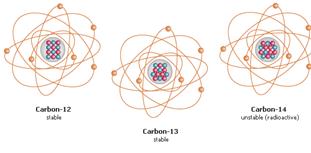
- Elements occur in nature as a mixture of ISOTOPES
ISOTOPES = atoms with the same number of protons
but differ in number of neutrons
EX: 14C , 13C, and 12 C all have 6 protons & 6 electrons,
but different numbers of neutrons
Most isotopes are stable (EX: 12C and 13C)
but some are radioactive (14C)
ENERGY LEVELS – 3-D space where electrons are found = ORBITAL
• Level closest to nucleus = lowest energy; outer levels have more energy
1st level- 1 orbital holds 2 electrons
2nd level- 4 orbitals hold 8 electrons
3rd and higher levels- hold increasing numbers of electrons
- EX: Lithium (3 ELECTRONS) has two in the first shell; one in second shell
- Neon (10 electrons) has two in the first shell; eight in second shell
CHEMICAL BEHAVIOR depends on number of electrons in OUTERMOST SHELL (=VALENCE electrons)
• Atoms with the same number of valence electrons have similar chemical behaviors
• Atom with a completed valence shell = nonreactive (EX: neon)
• Atoms with incomplete valence shells = chemically reactive
• Atoms can give up, accept, or share electrons in order to have a stable outer shell
ELEMENT |
# of |
Hydrogen |
1 |
Oxygen |
2 |
Carbon |
4 |
Nitrogen |
3 |
Phosphorus |
5 |
Sulfur |
2 |
MOLECULES= two or more atoms of SAME or DIFFERENT elements bonded together (EX: O2)
COMPOUNDS = two or more DIFFERENT elements bonded together (EX: H2O)
CHEMICAL FORMULA = recipe; tells which kinds of atoms and how many
EX: H20 = TWO Hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom
*change in characteristics when elements combine = EMERGENT property
TYPES OF BONDS
 1) COVALENT: share electrons
1) COVALENT: share electrons
• SINGLE- share a PAIR of electrons (shown as single dash H-O-H)
• DOUBLE- share TWO PAIRS of electrons (shown as C=C)
• TRIPLE- share THREE PAIRS of electrons (shown as  )
)
POLAR COVALENT BONDS - sharing of electrons = unequal;
seen in atoms with differences in electronegativity
one atom slightly more positive/other more negativity
NONPOLAR COVALENT BONDS- EX: methane
electron sharing is equally distributed
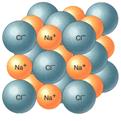
2) IONIC BONDS:
electrons are transferred from one atom to another (CATION =+ ANION =-)
+/- partners (IONS) are held together by attraction between opposite charges
EX: table salt (NaCl) Sodium loses one electron; Chlorine picks up one electron
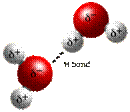
3) HYDROGEN BONDS: weak attraction between molecules or parts of same molecule
• slightly positive hydrogen atom of one molecule attracted to slightly negative atom in another
EX: water molecule- electrons spend more time orbiting oxygen than hydrogens
so oxygen becomes slightly negative and the two hydrogens become slightly positive
4) Van der Waals Interactions-
attractions between ever changing + and - “hot spots” in covalently bonded nonpolar molecules
EX: responsible for gecko’s ability to walk up a wall
* Relative strength of bonds: Covalent > Ionic > Hydrogen bond > Van der Waals forces
Individual bonds (ionic, hydrogen, van der Waals) are weak and temporary, but collectively they are strong and play important biological roles.
CHEMICAL REACTIONS- make and break chemical bonds
OXIDATION-REDUCTION:
• Oxidation = the loss of electrons (or loss of hydrogen atoms), a molecule that loses an electron is oxidized
• Reduction = the gain of electrons (or gain of hydrogen atoms), a molecule that gains an electron is reduced
• Chemical bonds are broken and reformed/atoms are rearranged.
Reactants → products
• Reactions must be “balanced” –Number and kind of atoms in reactants must = those in products
• Matter is conserved in a chemical reaction
• Chemical reactions rearrange matter; they do not create or destroy matter.
• Some chemical reactions go to completion (all the reactants are converted to products)
• Most chemical reactions = reversible (products in forward reaction become reactants in reverse reaction)
- EX: 3H2 + N2 <=> 2NH3
hydrogen and nitrogen combine to form ammonia, but ammonia can decompose to hydrogen and nitrogen - Initially, reactant concentrations are high, so they frequently collide to create products
- As products accumulate, they collide to reform reactants
- EQUILIBRIUM
- • RATE of formation of products = the RATE of breakdown of products (RATE NOT CONCENTRATION)
- • Products and reactants are continually being formed, but no net change in their concentrations
- • Concentration of reactants and products typically NOT EQUA; concentrations stabilize at a particular ratio
- MOLECULE’S BIOLOGICAL FUNCTION RELATED TO ITS 3-D SHAPE
• Molecule with 2 atoms =linear
• Water molecule is shaped like a V, two covalent bonds are spread apart at 104.5° angle - • Shape of bigger molecule determined by the positions of the electron orbitals shared by bonded atoms
- • CARBON- Formation of a covalent bonds leads to hybridization of the orbitals to four new orbitals in a tetrahedral shape
• Large organic molecules contain many carbon atoms with repeating tetrahedral pattern - MOLECULES WIH SIMIALR SHAPES CAN HAVE SIMILAR FUNCTIONS
- EX: morphine, heroin, and other opiate drugs = simiilar in shape so they can bind to the same receptors as natural signal
molecules called endorphins - Binding of endorphins to receptors on brain cells produces euphoria and relieves pain.
Opiates mimic these natural endorphin effects.
http://local.brookings.k12.sd.us/krscience/open/chemistryoflife.htm
Source: http://www.biologyjunction.com/chemistry%20notes%20kelly.doc
Google key word : Chemistry notes file type : doc
Author : not indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly.
Chemistry notes
If you want to quickly find the pages about a particular topic as Chemistry notes use the following search engine:
Chemistry
Chemistry notes
Please visit our home page
Larapedia.com Terms of service and privacy page
